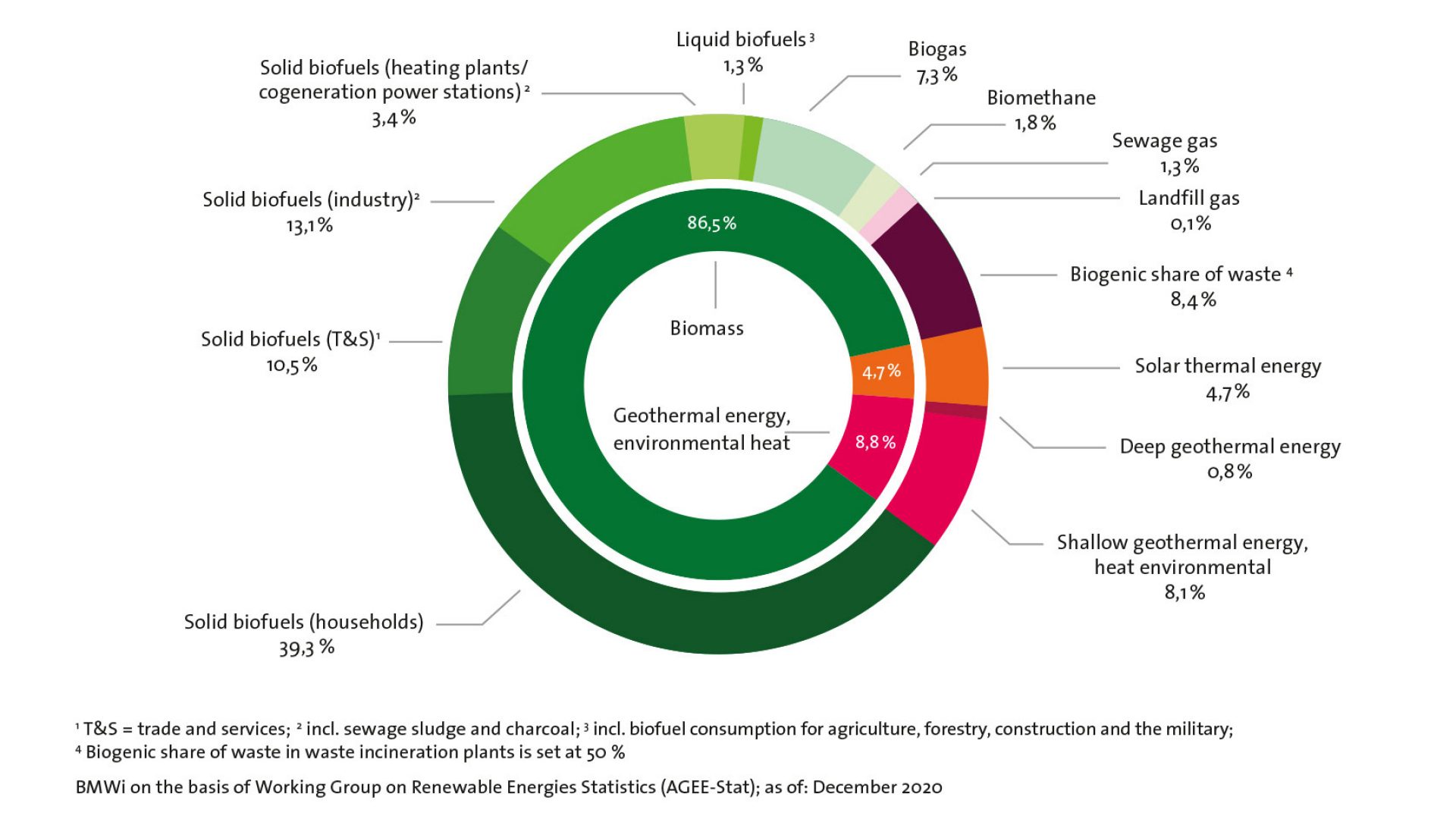
With 120 terawatt hours, wood heat supplies a good five percent of Germany's final energy consumption in a CO₂-neutral manner, which wind energy also comes close to achieving.
Largely domestic, sustainable and climate-friendly, wood heat makes the most important contribution of renewable energies in the heating market, which is accounting for over 50 % of Germany's final energy consumption. The increased use of modern combustion technologies as well as the replacement of outdated wood stoves, wood boilers and other emitters of particulate matter with state-of-the-art devices make it possible to reduce particulate matter emissions by up to 90 % while increasing energy efficiency by over 200 %.
Wood heat, an important part of the energy revolution
Wood energy secures around 45,000 jobs in Germany in a value chain from the energy source to the trade, the craft sector and the manufacturers of combustion technology. It is based predominantly on the use of residual wood that accumulates during timber harvesting or in sawmills. In addition, large quantities of damaged wood are used in the heating market, for example as a result of bark beetle infestation. This regional value addition of the use of wood for energy, across all its forms of application, already accounts for a large part of the climate protection impact with 36 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalents annually.
Potentials of wood heat
Wood is indispensable as an energy source. Primarily due to its climate friendliness and efficiency, it is already replacing classic fossil fuels in many places. As with all other renewable energies, there are advantages and disadvantages. As the means of choice to break away from fossil fuels, wood heat has many potentials:
- Wood is a renewable resource and almost CO₂-neutral.
- Wood is an important CO₂ sink.
- Wood strengthens regional value creation.
- The German forest is 100 % sustainably managed. The net growth of the available wood resources is about one to three percent per year.
- So far, only one third of the raw wood, about 15 million tonnes, is used for energy. There is still untapped potential here. Up to now, the use of wood in German forests has been around 20 million m3 per year below the sustainably usable increment.
- Wood can be used in different types of energy wood to operate differently designed heating systems: logs, wood chips, pellets or briquettes.
www.depi.de/pelletfachbetrieb-werden
Webseite Bundesverband Solarwirtschaft (BSW)
Informationsportal Sonnige Heizung
Pelletmagazin II/2020 PDF-Datei, ca. 16 MB
Heizen mit Holz – so geht’s richtig PDF-Datei, ca. 1 MB
Broschüre der Initiative Holzwärme „Holz, die große erneuerbare Energie“ PDF-Datei, ca. 2 MB